Permanent Tattoo Removal
Introduction
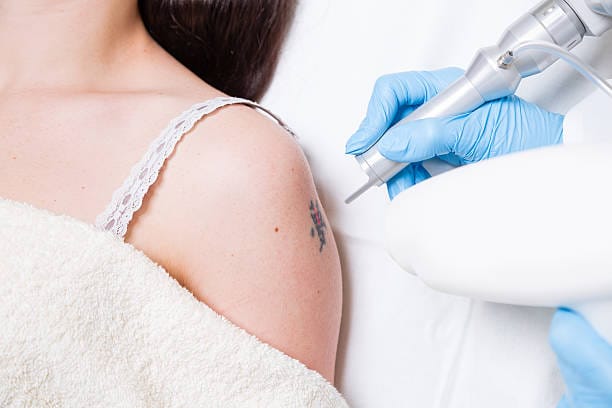
The process of removing a tattoo from the skin using different methods is known as permanent tattoo removal. In order for the body’s immune system to effectively remove the ink pigments from the skin, they must first be broken down. Most tattoos are removed using laser technology, which uses intense light pulses to disintegrate the ink particles in the epidermis. Chemical peels, dermabrasion, and surgical removal are additional treatments. The size, color, style of ink, and depth of the tattoo are just a few of the variables that affect how well a tattoo can be removed.
Pathophysiology
The breakdown and removal of ink pigments from the epidermis is a key component of the pathophysiology of irreversible tattoo removal. The most popular technique for tattoo removal uses laser technology. The tattoo ink pigments are broken down into smaller particles as a result of the laser’s high-energy light pulses, which are received by them. The immune system of the body absorbs the decomposed particles after which they are gradually removed by natural means.
The surrounding skin tissue is not affected as the laser only targets the ink pigments. The type and colour of ink used, the depth of the tattoo, and the patient’s skin condition all affect how well a laser tattoo removal procedure goes. Compared to light-colored ink, black and dark-colored ink is simpler to erase. The depth of the tattoo also affects how well the procedure works because deeper tattoos need more laser treatments to be completely removed. Other tattoo removal techniques, like dermabrasion, chemical peels, and surgical excision, literally remove the layer of skin that contains the tattoo ink. While these techniques can be successful, they may also leave scars and necessitate a lengthier healing period than laser tattoo removal.
Side Effects
The side effects of permanent tattoo removal depend on the method used for the procedure. However, some common symptoms include:
- Pain: Depending on the person’s pain threshold, the size, and the position of the tattoo, the removal of a tattoo can be excruciatingly painful.
- Swelling: One typical adverse effect of tattoo removal is swelling, which is brought on by the immune system’s reaction to laser or other removal techniques.
- Redness: Another typical side effect of laser hair removal is the possibility of redness and inflammation of the skin around the treated region.
- Itching: Some individuals may experience itching or a tingling sensation in the treated region. These symptoms can be soothed by using a cold compress or by taking painkillers.
- Scabbing: After tattoo removal, the treated region may develop scabs or crusts, which is a typical sign of the healing process.
- Blistering: Blistering is occasionally a sign of the body’s natural reaction to laser treatment or other techniques of hair removal.
How do Dermatologists do Permanent Tattoo Removal?
There are different techniques used by dermatologists for permanent tattoo removal, including:
- Laser Removal: The most popular and efficient tattoo removal technique is laser removal. High-intensity laser light is used to target the tattoo pigment and break it down into tiny particles that are then taken up by the body.
- Surgical excision: In this technique, the tattooed skin is removed and the adjacent skin is stitched back together. It can leave a scar and is usually used for small tattoos.
- Dermabrasion: In this technique, the top layers of skin, which contain the tattoo color, are removed using a high-speed rotary tool. Scarring and soreness are potential side effects.
- Salabrasion: This technique includes scrubbing the skin with an abrasive tool after applying a saltwater solution to the tattooed region.
Before & After Treatment Images