Ageing Changes
Introduction
The normal biological, physical, and psychological changes that occur as a person ages are called ageing changes. These changes may affect different bodily parts, which can also happen at varying rates depending on the person. Reduced bone density, altered vision and hearing, decreased muscle mass and strength, and altered skin elasticity and appearance are just a few of the physical changes commonly accompanying ageing.

Pathophysiology
The gradual decline of different physiological systems in the body is eventually caused by the complex interaction of genetic, cellular, and environmental factors that make up the pathophysiology of ageing. The following are some essential elements that affect the biology of ageing:
- DNA mutations and cellular damage: As we mature, our cells are more vulnerable to environmental pollutants, oxidative stress, and UV radiation damage.
- Telomere shortening: With each cell division, the protective caps on the extremities of our chromosomes, known as telomeres, get smaller.
- Mitochondrial dysfunction: Our cells’ powerhouses, the mitochondria, are in charge of producing energy.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation is a sign of ageing and can factor in various age-related illnesses, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological conditions.
- Hormonal changes: As we get older, our amounts of vital hormones like growth hormone, estrogen, and testosterone may drop, which can affect our metabolism, our body’s composition, and our general health.
Here are some standard diagnostic tests and assessments used in ageing:
- Physical examination: A thorough physical examination can help spot ageing-related changes in the cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal, and neurological systems, among other bodily systems.
- Laboratory tests: Blood, urine, and other tests can be used to track chronic conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, as well as to assess general health.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and other examinations can aid in the identification of age-related conditions like osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and neurological disorders.
- Cognitive evaluations: Evaluations of cognitive abilities, such as the Mini-Mental State Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, can help spot changes in memory, concentration, and other cognitive abilities brought on by ageing and dementia.
- Functional tests: Tests of functionality like the Timed Up and Go and the 6-Minute Walk.
Overall, ageing is not considered a specific medical disease but a regular and ongoing process.
Signs and Symptoms
Everyone ages naturally and experiences skin ageing as they age. The following are some typical signs of ageing skin:
- Fine lines and wrinkles: As skin ages, it becomes thinner and loses elasticity, which causes the formation of fine lines and wrinkles, particularly on the face, neck, and hands.
- Sagging skin: As we age, the structural underpinnings of our skin deteriorate, resulting in sagging skin, particularly around the cheekbones and jawline.
- Age spots and hyperpigmentation: Age spots and hyperpigmentation on the skin can form over time due to exposure to the sun and other environmental variables.
- Dryness and rough texture: Older skin generates fewer natural oils, which causes dryness and a rough texture.
- Lessened skin volume: As we age, the underlying muscle and fat tissue of our skin may weaken, which can result in a loss of skin volume, particularly in the cheekbones and temples.
- Skin thins: As we age, our skin gets thinner and more fragile, making it more prone to harm and injury.
- Increased susceptibility to infections and skin diseases: Aging skin is more susceptible to infections and skin diseases, including skin cancer.
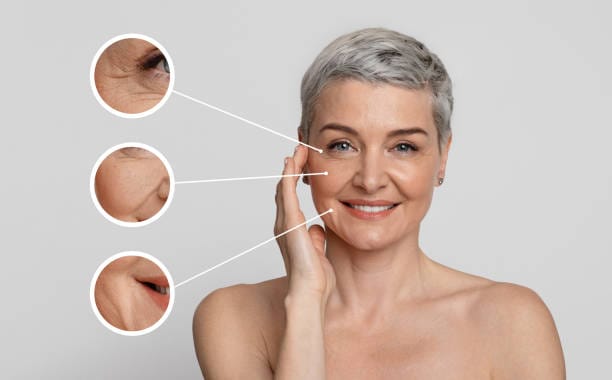
How do Dermatologists treat Skin Ageing?
Dermatologists use a variety of approaches to treat skin ageing, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s individual needs. Here are some common treatments for skin ageing:
- Topical treatments: To help improve skin texture, lessen fine lines and wrinkles, and boost collagen production, dermatologists may recommend topical creams or gels that contain retinoids, antioxidants, or other chemicals.
- Injectable procedures: Botox and dermal fillers are well-known injectable procedures used to smooth out wrinkles, add volume to the face, and improve facial features.
- Chemical peels: A chemical solution is applied to the skin during a chemical peel, which exfoliates the skin’s outer layer and encourages the development of new, healthy skin cells.
- Laser and light therapies: IPL (intense pulsed light) and fractional laser resurfacing are two laser and light treatments that can help to lessen the appearance of age spots, fine lines, and other signs of ageing on the face.
- Surgical procedures: In some circumstances, dermatologists may suggest surgical procedures to address more pronounced symptoms of skin ageing, such as facelifts, brow lifts, or eyelid surgery.
Before & After Treatment Images