Hair Transplantation
Introduction
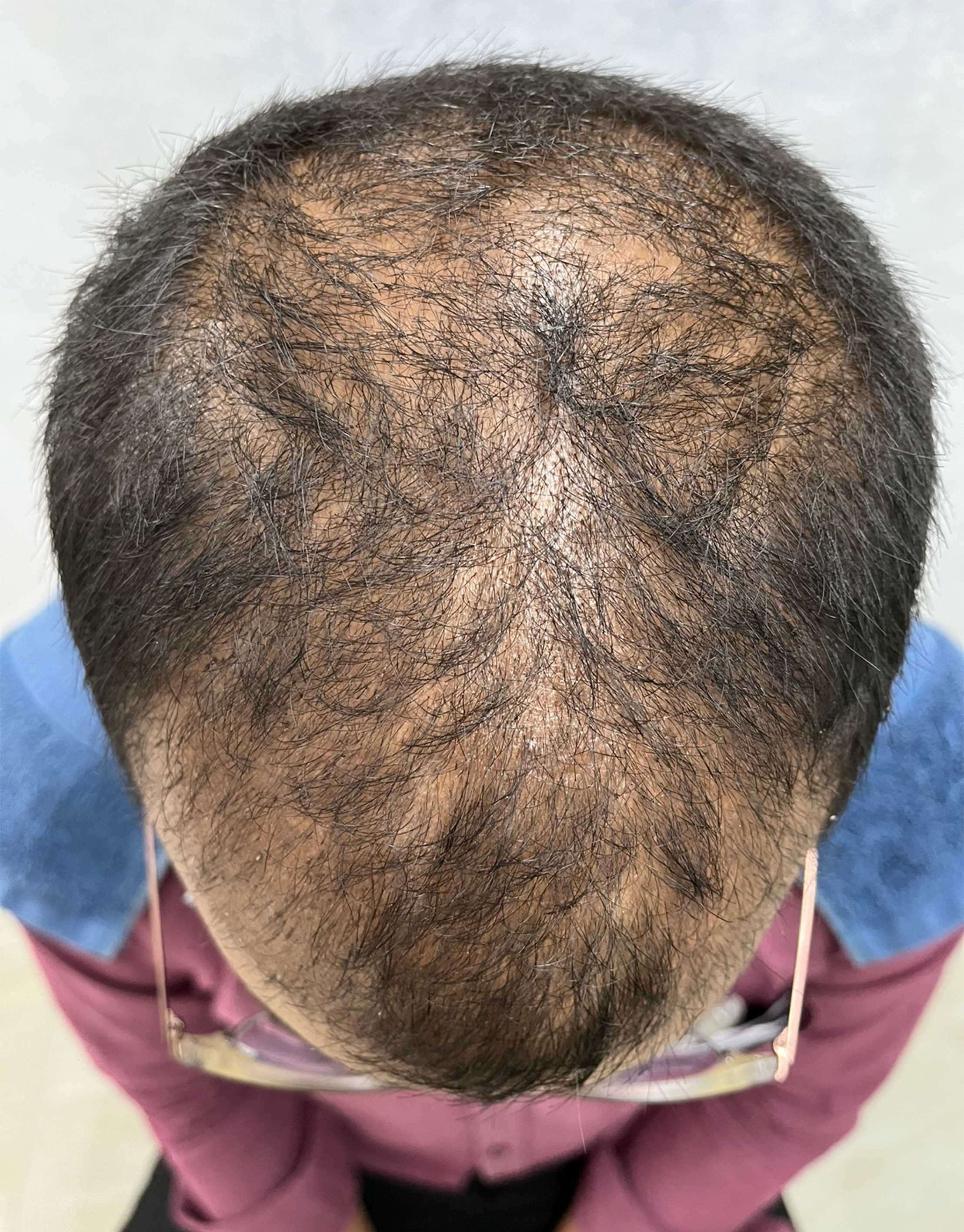
Hair follicles from a donor area, usually the back of the head, are removed during a surgical process called a hair transplant and then transferred to a scalp area that is bald or thinning. Male pattern baldness is the most prevalent condition that the procedure is used to treat, but it can also be used to treat hair loss in women or to treat hair loss brought on by trauma or medical treatments.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction are the two primary methods used for hair transplantation. (FUE). In FUT, a strip of skin is taken from the donor region and divided into individual follicular units before being transplanted to the recipient area. On the other hand, FUE entails the direct extraction of individual follicular units using a specialised punch tool from the donor area, which are then transplanted to the recipient region.
Pathophysiology
The transplanted hair follicles are typically taken from the sides or back of the scalp because those regions of the scalp have hair that is more resistant to balding and are then placed in the desired locations on the scalp for hair growth. The transfer of hair follicles, which contain the cells necessary for hair development, is a key component of the pathophysiology of hair transplantation. From the donor region, hair follicles are carefully removed before being transplanted into the recipient area. After transplantation, the follicles start to produce new hair, which can give the appearance of a thicker, more natural head of hair. To get the desired results, the process might take several hours and involve multiple sessions.
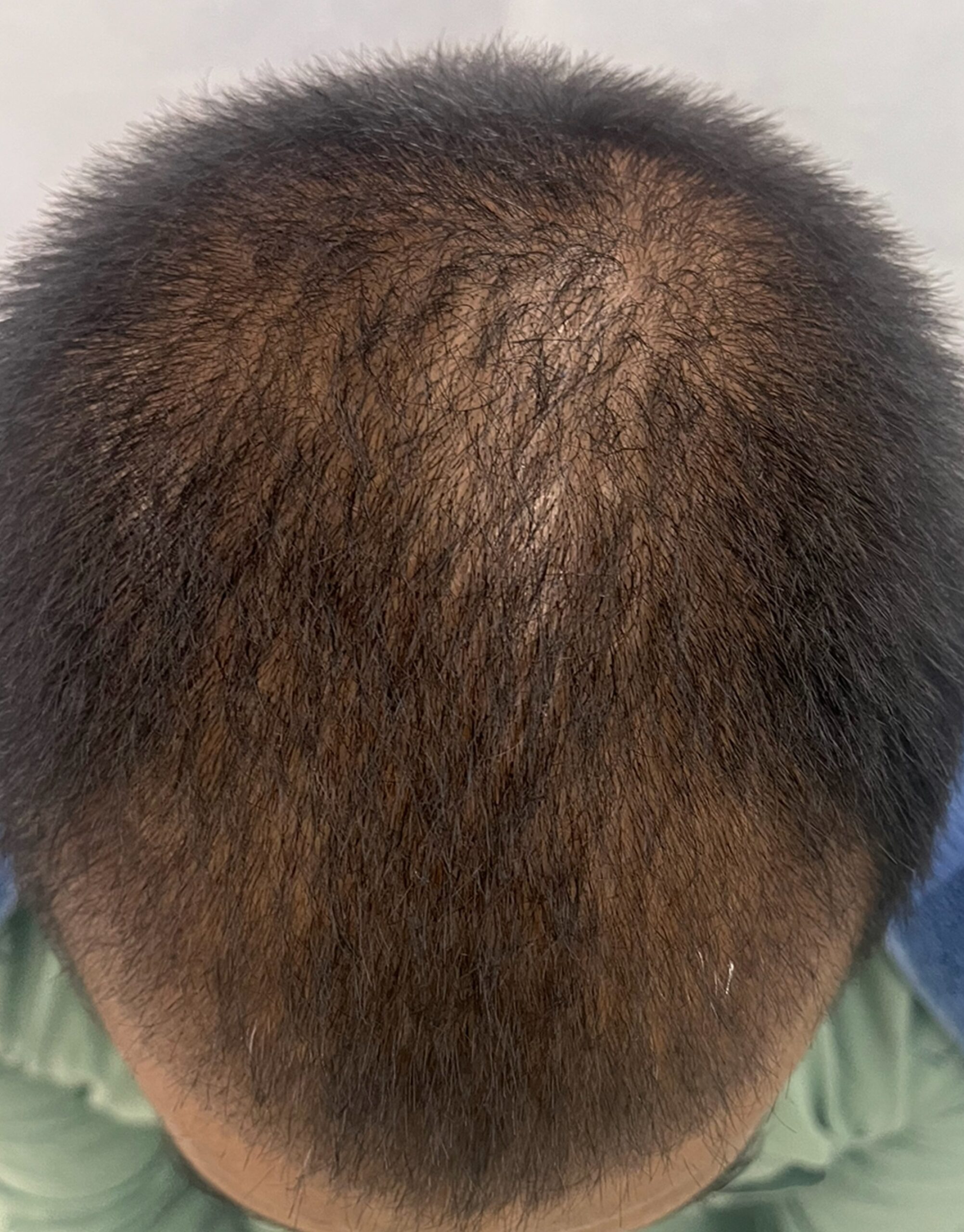
Before new hair development starts after the hair transplant, the transplanted hair follicles may shed for a while. This natural process step, which usually takes place in the first two to three weeks following the operation, involves shedding. The new hair may not begin to grow for several months, and the complete effects might not become apparent for up to a year. In order to achieve the best results, ongoing hair care and maintenance are necessary because the transplanted hair will continue to grow and act like natural hair.
Side Effects
After a hair transplantation procedure, some common side effects can be expected, including:
- Pain or discomfort in the scalp region: For a few days after operation, patients may feel tightness, pain, or discomfort in the scalp area.
- Swelling: Following the treatment, the scalp may swell. Usually, swelling reaches its peak on days three or four and then steadily goes down over the course of a week.
- Bruising: Minor bruising or discoloration around the hairline or forehead is possible in some people, but this usually goes away on its own after a week or two.
- Scabbing: Around the newly transplanted hair follicles after the hair transplant process, small scabs may develop. Within a week or two, these usually fall off on their own.
- Itching: Patients may feel tingling or itching in the regions that have been treated. 5. Itching: As the hair follicles recover, patients may feel tingling or itching in the treated regions.
- Shock loss: Hair loss is common in the weeks after a hair transplant because the transplanted hair follicles go through a dormant period before beginning to grow again. This is referred to as “shock loss” and is ordinarily transient.
- Numbness: For a few weeks after the procedure, patients might feel numb or have no sensation in the region that was treated.
How do Dermatologists do Hair Transplantation?
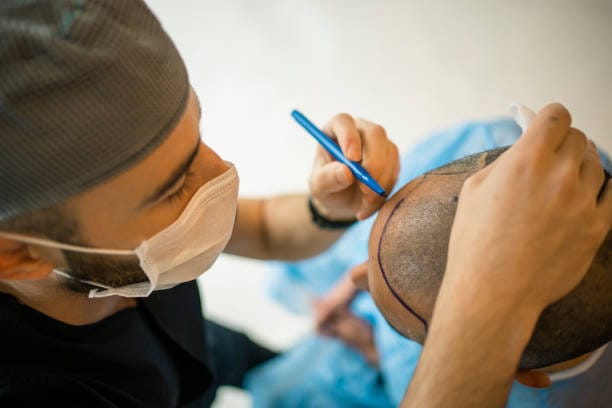
A dermatologist or a hair transplant surgeon will conduct the surgical procedure known as hair transplantation. The process entails removing healthy hair follicles from the donor area, which is the back or sides of the scalp, and transplanting them to the scalp’s bald or thinning areas. Local anaesthesia is typically administered to numb the scalp to begin the process. The surgeon then uses a specialised tool, such as a micro punch, to remove hair follicles from the donor region. Under a microscope, the extracted hair follicles are then prepped for transplantation.
The prepared hair follicles are carefully transplanted into these tiny incisions or slits made in the recipient region by the surgeon using a specialised instrument. To produce a hairline that looks natural, the surgeon takes care to position the transplanted hair follicles at the proper angle and in the proper direction. Depending on the degree of hair loss and the quantity of hair follicles that need to be transplanted, the entire process could take several hours. The patient might experience some minor swelling and discomfort following the treatment, but these side effects can be treated with painkillers and cold compresses. To ensure proper healing and the best outcomes, it’s crucial to adhere to the surgeon’s post-operative care directions.
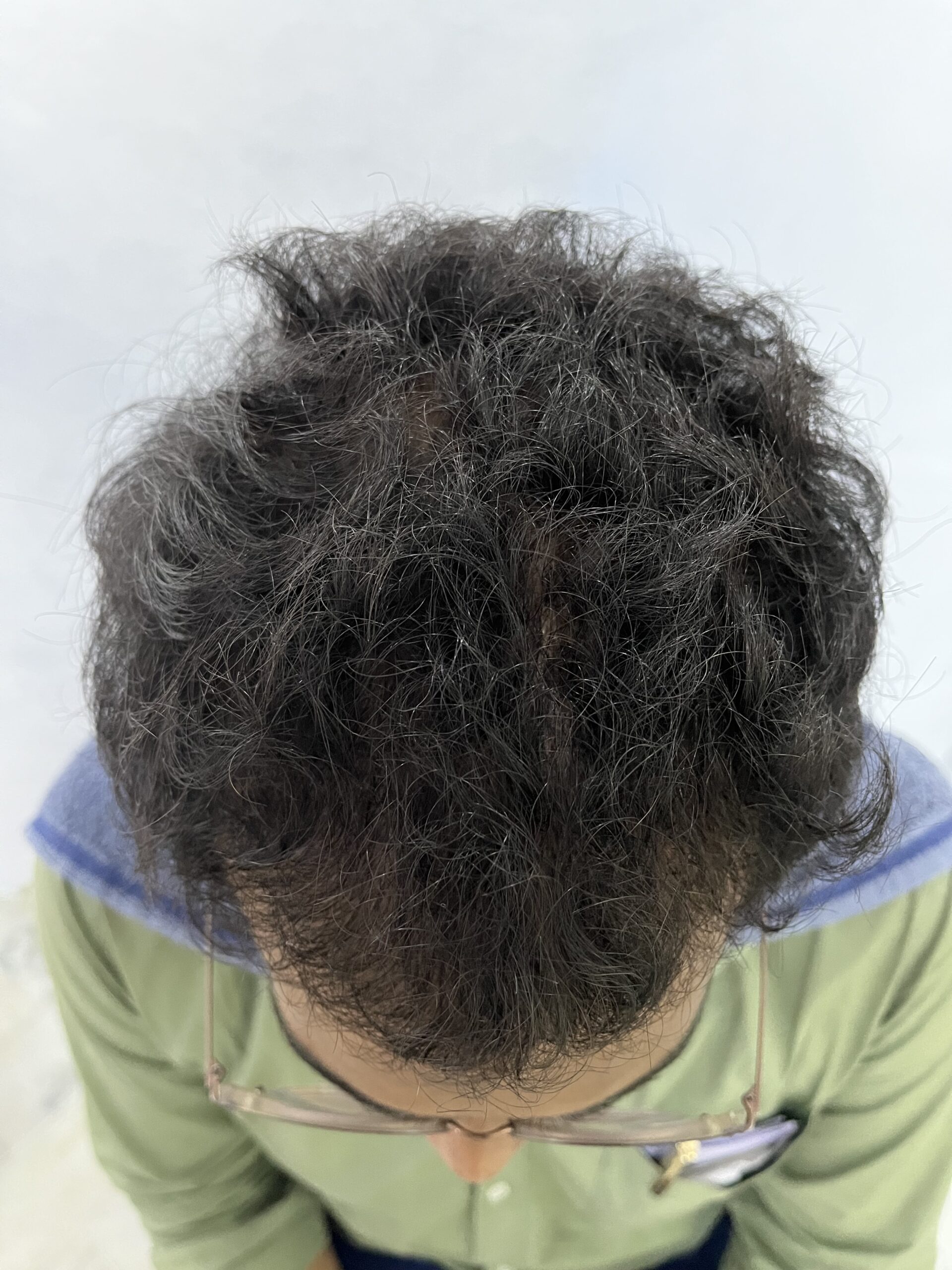
Before & After Treatment Images