Botox
Introduction
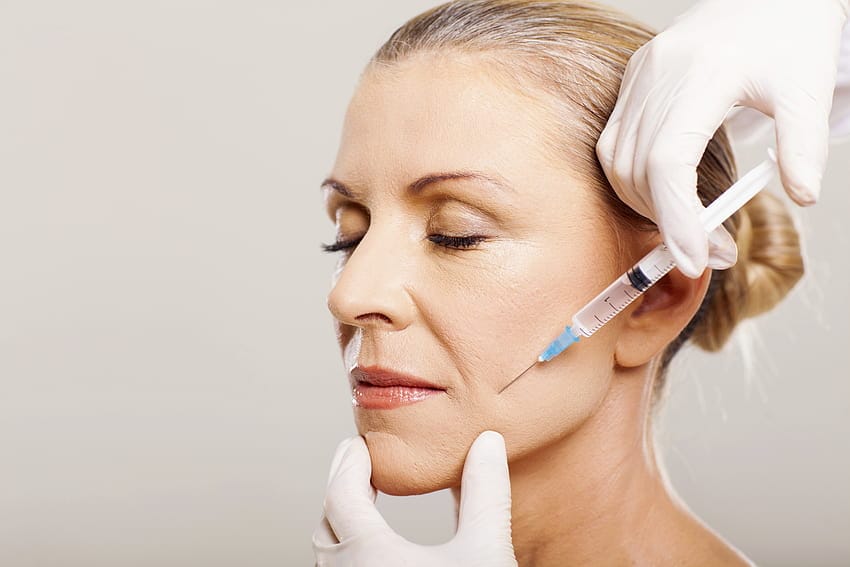
A purified form of the botulinum toxin made by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum is sold under the trade name “Botox.” Botox briefly paralyses or weakens muscles when injected into them by obstructing nerve signals. Multiple medical and aesthetic problems, such as muscle spasms, migraines, excessive sweating, and wrinkles, can be treated with this. Botox is most frequently used for cosmetic purposes to smooth out wrinkles and fine lines on the face, especially on the forehead, in the space between the brows, and around the eyes. It is possible to repeat the injections as necessary to keep the desired results. The effects of Botox injections usually last for several months before gradually wearing off.
Pathophysiology
Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that transmits signals between nerves and muscles, is what Botox targets in order to function. When acetylcholine is not allowed to leave the muscles after a Botox injection, the muscles become momentarily weak or paralysed. According to the pathophysiology of wrinkles, repeated muscular contractions can cause the skin to wrinkle and develop fine lines over time. Botox can lessen wrinkles and fine lines by momentarily weakening or paralysing the muscles that cause these spasms.
Where facial wrinkles and fine lines are most prevalent, Botox injections are usually given into the muscles of the forehead, in the space between the eyebrows, and around the eyes. The injections can be repeated as often as necessary to keep the desired results. The effects of Botox usually last for several months before gradually wearing off. When administered by a qualified healthcare professional, Botox is generally regarded as safe, but there are some possible risks and side effects, including temporary bruising, swelling, and redness at the injection site, as well as headache, flu-like symptoms, and muscle weakness in rare instances.
Side Effects
When administered by a qualified healthcare expert, Botox injections are generally regarded as safe, but there are possible risks and side effects. Following are some typical side effects of Botox injections:
- Short-term redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection location
- Indicators of the illness or a headache
- A brief drooping of the eyebrow or eyeball
- Excessive tearing or dry eyes
- Light sensitivity or impaired vision
- Speaking or swallowing difficulties
- Muscle aches or immobility in other parts of the body
- Allergic responses like hives, a rash, or itching
How do Dermatologists do Botox?
Dermatologists and other trained healthcare professionals typically follow a specific process when administering Botox injections:
- Consultation: The doctor will first visit with the patient to hear about their concerns, medical background, and any prescription drugs or dietary supplements they may be taking. This will aid in deciding if Botox is the best course of action.
- Preparation: The medical expert will make the Botox solution by saltwater dilution.
- Injection: The medical expert will inject the Botox solution into the desired muscles using a tiny needle. To lessen pain, they might first administer a numbing cream or an ice pack to the area.
- Post-injection care: The healthcare provider will give the patient directions on how to take care of themselves after an injection, such as not touching or rubbing the injection site and refraining from strenuous activity for a while.
Before & After Treatment Images